Differences Between Energy-Saving Synchronous Motors and Conventional Motors
 Nov 17, 2023|
Nov 17, 2023| View:172
View:1721. Operating Principles:
Conventional Motors:
Conventional motors, such as induction motors, operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. They rely on the interaction between magnetic fields to generate rotational motion. These motors require an external power source to create a rotating magnetic field, which in turn drives the rotor.
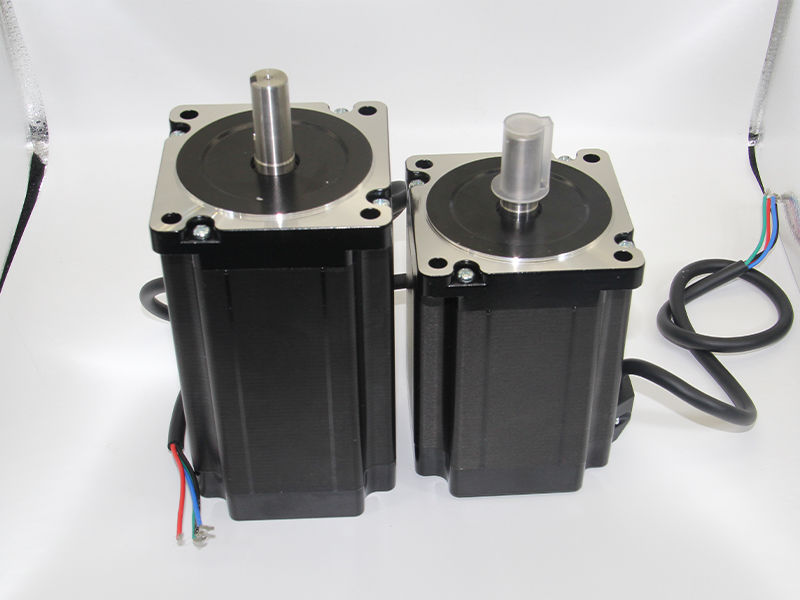

Energy-Saving Synchronous Motors:
Energy-saving synchronous motors operate on the principle of synchronous operation. These motors have permanent magnets embedded in the rotor, which create a constant magnetic field. The stator's magnetic field synchronizes with the rotating magnetic field of the rotor, resulting in highly efficient operation.
2. Efficiency:
Energy efficiency is a crucial factor when comparing motors. Energy-saving synchronous motors have higher efficiency compared to conventional motors. The absence of rotor losses, reduced copper losses, and improved power factor contribute to their higher efficiency. This improved efficiency leads to substantial energy savings, especially in continuous operating applications.
3. Power Factor:
Power factor is a measure of how effectively a motor converts electrical power into useful mechanical power. Conventional motors often have a lower power factor, which leads to increased reactive power consumption and higher energy costs. In contrast, energy-saving synchronous motors have a higher power factor, resulting in improved electrical efficiency and reduced power consumption.
4. Applications:
Conventional Motors:
Conventional motors are widely used in various applications, including pumps, fans, compressors, and conveyors. They are suitable for applications that do not require precise speed control or high energy efficiency.
Energy-Saving Synchronous Motors:
Energy-saving synchronous motors are often preferred in applications that demand high energy efficiency and precise speed control. These motors find application in industries such as HVAC systems, industrial machinery, robotics, and electric vehicles. They are particularly beneficial in applications with variable loads, where energy consumption can be optimized through speed control.
5. Cost Considerations:
Energy-saving synchronous motors typically have a higher initial cost compared to conventional motors. However, the long-term energy savings and improved efficiency often outweigh the higher upfront investment. The return on investment (ROI) for energy-saving synchronous motors can be realized through reduced energy consumption and lower operating costs over the motor's lifespan.
Energy-saving synchronous motors offer significant advantages over conventional motors in terms of efficiency, power factor, and precise speed control. While they may have a higher initial cost, the long-term energy savings and improved performance make them a viable choice for applications that prioritize energy efficiency and sustainability. As industries continue to emphasize energy conservation, the demand for energy-saving synchronous motors is expected to increase in various sectors.